Why is Grain Stored in Silos?
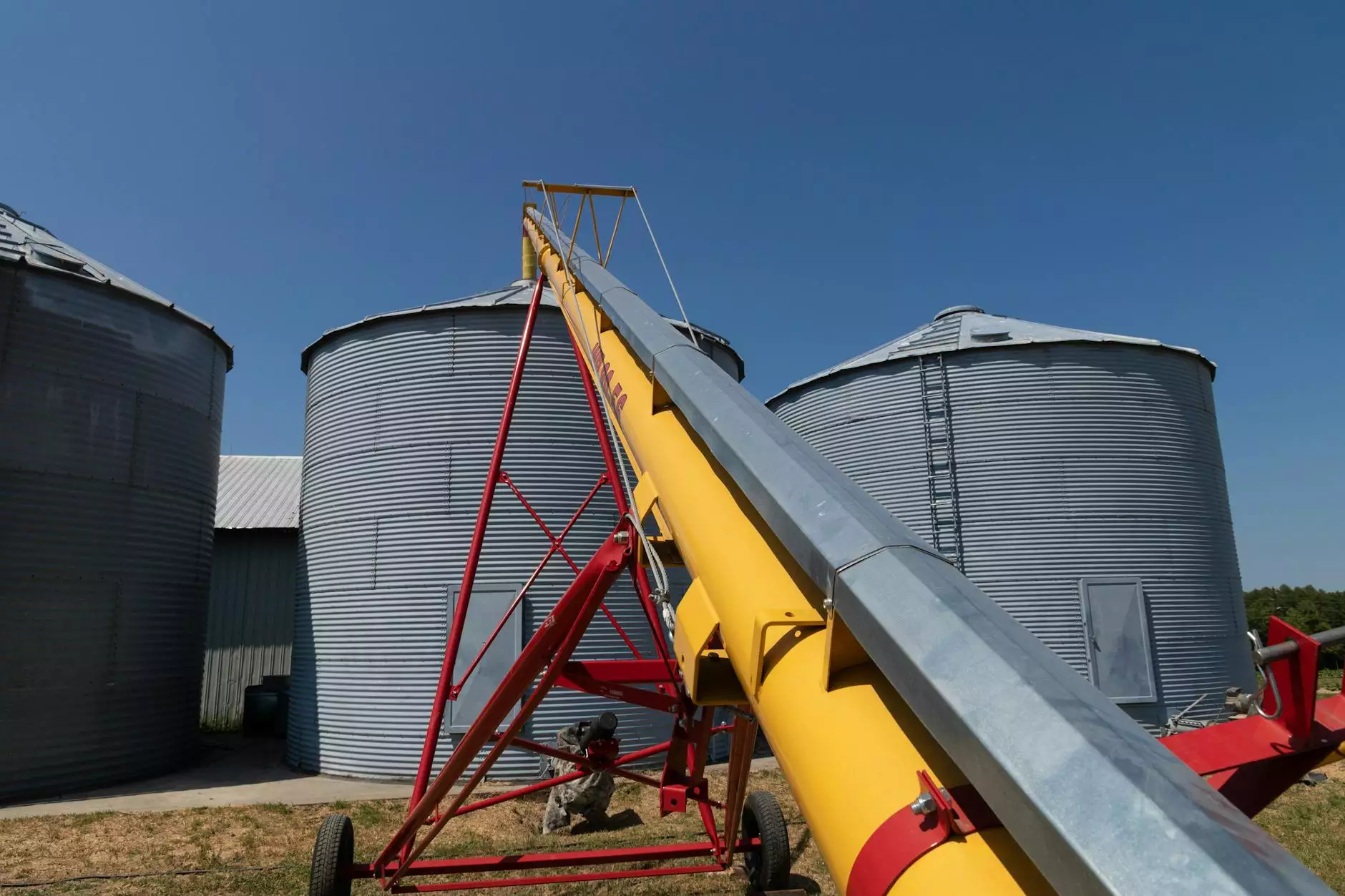

Grain storage is a critical aspect of agriculture that has profound implications on food security, farmers’ profitability, and supply chain management. Among the various methods of grain storage, silos have emerged as the most prevalent and effective choice for farmers and grain companies alike. In this article, we will delve deep into the reasons why grain is stored in silos, exploring both the practical benefits and the technological advancements that have revolutionized grain storage in modern agriculture.
The Importance of Grain Storage
Before we address why is grain stored in silos, it’s essential to understand the significance of grain storage in the overall agricultural process. Proper storage is crucial for the following reasons:
- Preservation of Quality: Grain can deteriorate rapidly if not stored correctly. Moisture, pests, and temperature fluctuations can lead to spoilage. Silos provide a controlled environment that minimizes these risks.
- Extending Shelf Life: By storing grains in silos, farmers can extend their viability for months or even years. This ensures that grains can be sold at optimal prices rather than during harvest when prices are typically lower.
- Facilitating Marketing: Grain can be stored until market conditions are favorable, allowing farmers to maximize their profits.
The Functionality of Silos
Silos are specially designed structures that provide an ideal environment for grain storage. They come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored to specific types of grains and storage needs. The main functionalities of silos include:
- Controlled Environment: Silos are designed to protect grain from external elements such as rain, sun, and pests, thereby maintaining a stable temperature and humidity level.
- Efficient Loading and Unloading: Modern silos are equipped with advanced technology that allows for quick and efficient loading and unloading of grain, reducing labor costs and time.
- Automated Monitoring: Many silos are fitted with sensors that monitor grain conditions, alerting farmers to any potential issues before they become serious problems.
Benefits of Storing Grain in Silos
Understanding why is grain stored in silos also involves recognizing the numerous benefits these structures provide:
1. Protection Against Pests and Spoilage
One of the primary reasons for using silos is their effectiveness in protecting stored grain from pests and spoilage. Silos are built to be airtight, which restricts the entry of insects and rodents, thereby safeguarding the quality of the grain.
2. Space Optimization
Farmers often face challenges related to space when storing large quantities of grain. Silos can store more grains in a smaller footprint compared to traditional storage systems such as warehouses. This allows for better use of land and efficient management of storage space.
3. Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in a silo may be significant, the long-term savings on operational costs can be substantial. Reduced spoilage, minimized pest control costs, and decreased labor needs all contribute to a more profitable operation.
4. Energy Efficiency
Modern silos are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Many are equipped with cooling systems that require less energy than traditional grain storage methods, making them an environmentally friendly option.
Types of Silos
There are various types of silos used in grain storage. Understanding these types is essential for farmers to make informed decisions depending on their specific needs:
1. Concrete Silos
These are among the most durable options available. Concrete silos are strong, weather-resistant, and can be constructed to any height. However, the initial construction cost is relatively high.
2. Steel Silos
Steel silos offer experts the advantage of being lightweight and easy to install. They provide excellent protection against pests, and their smooth surfaces help minimize grain damage during handling.
3. Fabric Silos
Fabric silos are an increasingly popular option among farmers looking for a flexible and cost-effective storage solution. They are easy to transport and set up, making them ideal for temporary storage needs.
4. Bunker Silos
Bunker silos are typically used for larger quantities of grain, particularly for crops like corn and silage. They are often built into the ground and covered to protect against the elements.
Technological Advances in Silo Storage
As agriculture evolves, so do the technologies that support it. Heavily reliant on technology, modern silos benefit from advancements that improve efficiency and grain quality:
1. Smart Silo Systems
Today’s silos can be equipped with smart monitoring systems that provide real-time data about grain conditions. These systems can alert farmers to changes in temperature or humidity, helping them maintain optimal storage conditions.
2. Automated Grain Handling Systems
Automation has transformed the way grain is handled in silos. Automated loading and unloading processes reduce the need for manual labor, resulting in cost savings and increased efficiency.
3. App-Connected Silos
Some modern silos come with app connectivity allowing farmers to monitor their grain storage from their smartphones. This convenience enables farmers to manage their grain better, even when they are not physically present at the site.
Challenges in Silage Management
Despite their advantages, managing grain storage in silos doesn’t come without challenges:
1. Initial Investment Costs
The upfront costs for purchasing and installing silos can be a substantial barrier for some farmers. This is especially true for smallholders who may have limited capital to invest in such infrastructure.
2. Maintenance Requirements
While silos are built to last, they do require regular maintenance to ensure they continue functioning efficiently. Neglecting maintenance can lead to significant issues, including grain spoilage and structural failures.
3. Risk of Grain Spoilage
While silos help reduce spoilage, they are not foolproof. Improper management, such as failing to monitor temperature and moisture levels, can result in spoilage even in silo storage.
Best Practices for Grain Storage in Silos
To maximize the benefits of storing grain in silos, farmers can follow these best practices:
- Regular Monitoring: Utilize technology to routinely check the conditions within the silo and ensure they are optimal for grain storage.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Efficient air circulation within silos is vital to prevent heat buildup and maintain consistent moisture levels.
- Implement Strict Hygiene Protocols: Regularly clean silos to prevent contamination from pests or mold.
- Educate Staff: Proper training for all staff involved in grain management ensures that everyone understands the importance of proper silo operation.
Conclusion
In summary, the question of why is grain stored in silos is answered through understanding the multifaceted advantages they bring to grain storage. From protecting against spoilage and pests to facilitating better market timing, silos are indispensable tools in modern agriculture. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and adhering to best practices, farmers can maximize their investments in silos, ultimately enhancing their productivity and offsetting the challenges that arise in grain management.
For those involved in Farm Equipment Repair or seeking quality Farming Equipment, visit tsgcinc.com to explore various solutions tailored to your agricultural needs. The future of agriculture hinges on effective grain storage, and silos are at the forefront of that evolution.